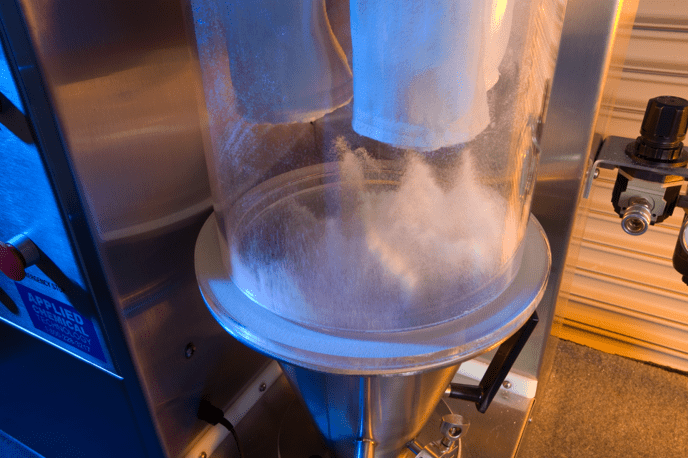
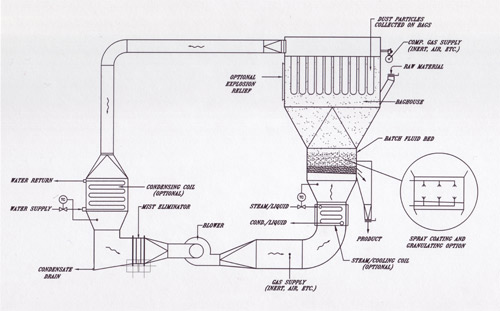
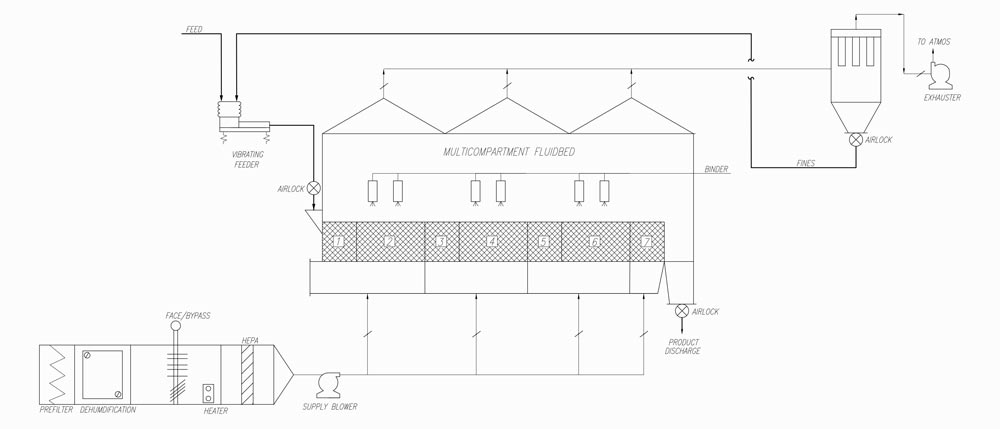
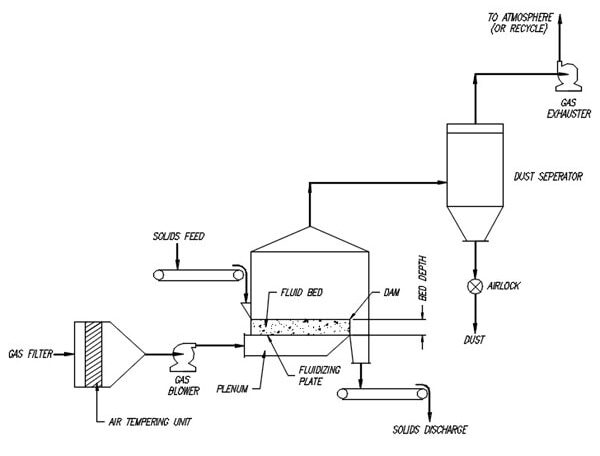
A fluidized bed (or simply fluid bed) is a bed or layer of solid particles that are treated in such a way that they behave like a fluid. This may occur either by mechanical means (vibration) or by the upward thrust of a fluid on the solid particles. The term fluid bed is also used for the piece of equipment designed to produce a fluidized bed within it. The most efficient and dependable industrial fluid beds are the types that rely on a fluid stream to suspend the solid. This fluid stream can be either a liquid or a gas. For the rest of this discussion, we will focus on fluid beds using gases to produce fluidization.
Fluid beds come in a wide range of sizes, materials, and configurations based on the application for which they are used. For example, they may be constructed of carbon steel, stainless steel, specialty alloys, and more. Additionally, they be designed to be used for batch processes or continuous processes. Their sizes are usually given in terms of the area of the bed or the capacity of the material they can process. A bench scale fluid bed can be small as 1/4 ft2 and commercial scale fluid beds as large as 100 ft 2 or more. Typical capacities for fluid beds are anywhere from 2 lbs/hr to 50 tons/hr.