Demystifying the Engineering Process-Part 2
Basic Engineering
Why Do Basic Engineering? Basic Engineering (sometimes called Front End Engineering) adds another layer of detail to the Preliminary Engineering package and is performed to refine the cost estimate from the first phase and to provide the information for an invitation for bids. At completion of the Basic Engineering Package the plant design is considered approximately 30% complete and the cost estimates of the equipment are within an error of 10% and the total cost estimate of the plant is good to within plus 15% to 30%. The Basic Engineering Package will provide enough information to allow an informed decision to proceed with the project. Often smaller companies will choose to omit the Basic Engineering Phase to save costs and instead go directly from the Preliminary Engineering Phase to the Detailed Engineering Phase. When Do Basic Engineering? Basic engineering is done after completing the Preliminary Engineering Package. The Basic Engineering Phase typically includes any Pilot Plant Testing that was identified as needed during preliminary engineering. What to Expect Typical Time to Complete Phase: 10-12 weeks The following are addressed during Basic Engineering:
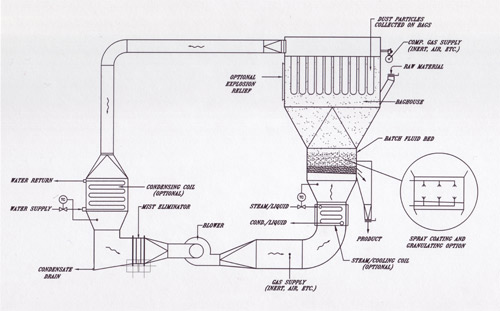
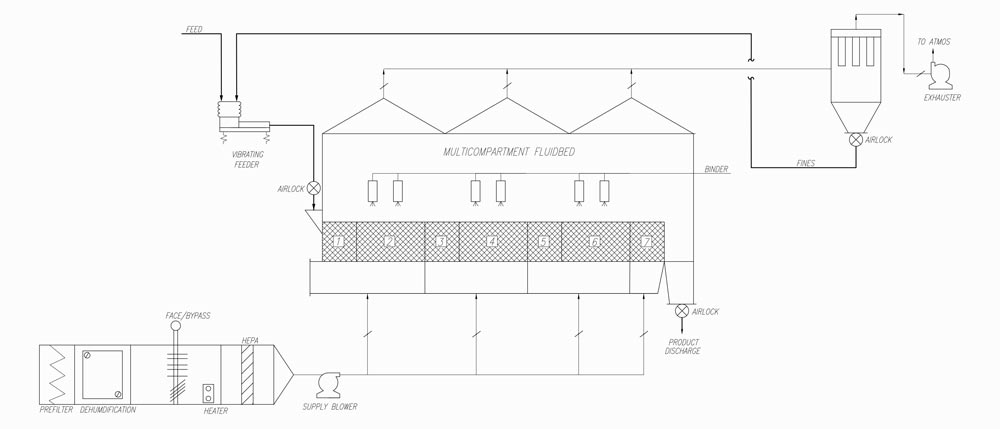
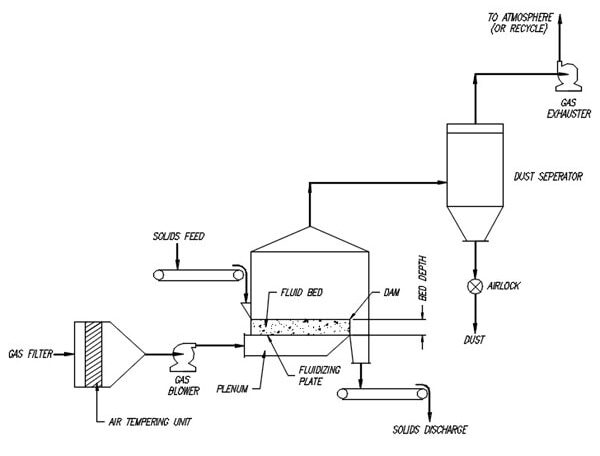
- Flowsheet – Drawing showing process flow and all pieces of equipment
- Heat and Material Balance – Material balance of each component, includes flow rates, temperatures, pressures, pressure drops associated with each piece of equipment
- Preliminary Utility Balance
- Process Description including Control Philosophy – Write up describing how the process works and general control logic
- Layout Drawings / System Design – Detailed depiction of how the system will fit together and layout of all pieces of equipment with dimensions, includes elevation and plan views
- P & ID’s – Drawings showing process with all instruments including valves, controls, switches, interlocks, etc, as well as duct sizes and pipe sizes
- Equipment List – List of the equipment to be used in the process
- Equipment Specifications – Detailed description of all the equipment that needs to be purchased or fabricated, with required capacities, recommended manufacturers, and model numbers
- Instrument List – List of all the instruments used in the process, such as valves, flow meters, motors, etc.
- Instrument Specifications – Detailed description of all the instruments that need to be purchased, with required process parameters, recommended manufacturers, and model numbers
- Preliminary Control System Design – A detailed description of the control scheme and logic, control system platform, etc.
- Emergency Shutdown Philosophy
- Cause and Effects Diagrams
- Duct Specifications – Duct material of construction, connections, temperature and pressure ratings
- Insulation Specifications – Heat transfer and load calculations, insulation recommendations
- Horsepower List – Equipment list with motor sizes for each piece
- HAZOP and HAZID
- Preliminary Fire and Water Demand Calculations
- Safety Philosphy
- Environmental Impact Assessment
- General Arrangement Drawings
- 3D Model Review – Equipment and main process line only
- Concept of Loading / Unloading with Drawing – Detailed description and dimensioned drawings of loading and unloading methods for the system
- Project Schedule – Proposed schedule for the detailed engineering and fabrication phase
- +/- 15% to 30% Cost Estimate for Final System Design and Engineering
Optionally included:
- Buildings/foundations
- Steam boiler or other utility equipment that may already be present at the facility
- Product storage or packaging
- Electrical power supply design
What’s Next? At the completion of the Basic Engineering Phase of a project, the design is approximately 30% complete. This is enough detail to solicit bids for the plant with a confidence level of 15-30%. Basic engineering is followed by Detailed Engineering during which the design completed and bids made to fabricate and construct the plant. Following the completion of this phase, the owner chooses one or more of the following: